In today’s tech-driven world, terms like “LLM” seem to pop up everywhere, especially in discussions about artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. But if you’re scratching your head wondering what exactly an LLM is, you’re not alone. Let’s dive in and unpack the mystery behind LLMs—what they are, how they work, and why they’ve become such a big deal in technology.
At its simplest, an LLM stands for Large Language Model. These models are a type of AI designed to understand and generate human-like language. To do this, they are trained on huge amounts of text—everything from books and websites to social media posts and more. Because of this, LLMs can answer questions, help write text and even have conversations with people in a way that feels very natural.
The “large” part of LLM refers to the fact that these models are made up of billions, or even trillions, of parameters. Think of parameters as the building blocks of the model that help it make decisions. The bigger the model, the more data it can handle, allowing it to understand language on a much deeper level.
How Do LLMs Work?
LLMs use a learning process known as unsupervised learning, which means they learn by reading tons of text and predicting what comes next in a sentence. Imagine you’re reading a sentence like “The cat sat on the ___,” and the LLM needs to figure out that “mat” is a likely word to complete it. By doing this over and over, the model starts picking up on the rules of grammar, word relationships, and even more subtle things like tone or cultural context.
One key technology that powers LLMs is called a transformer, a type of neural network introduced in 2017. Transformers allow the model to focus on different parts of a sentence at the same time, instead of reading it one word after another. This makes it better at understanding complex ideas and contexts within language, which is why modern LLMs are so much smarter than earlier models.
How are large language models trained?
Training Large Language Models (LLMs) is a complex process. It involves feeding the model massive amounts of text data and using a technique called self-supervised learning. Here’s a simplified explanation:
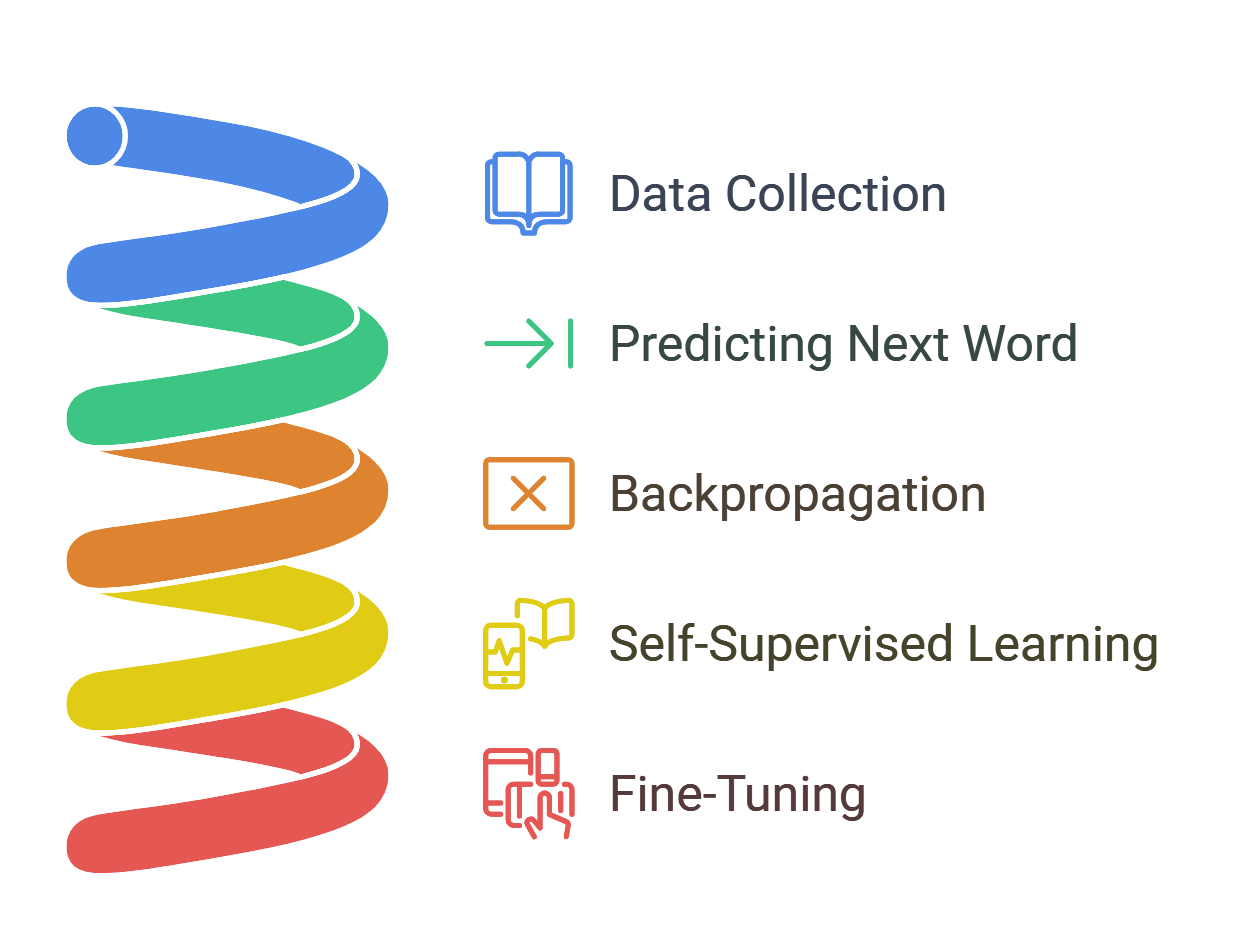
1. Data Collection
The first step in training an LLM is feeding it a vast amount of text data. This data comes from books, articles, websites, and other written content. The model uses this information to learn the structure, grammar, and patterns of language.
2. Predicting the Next Word
Once the model has this data, its primary task is to predict the next word in a sequence of words. For example, if the model is given the sentence “The sun is shining and the birds are __,” it would need to predict the missing word (e.g., “singing” or “chirping”).
At first, the model doesn’t know the right answer and might make random guesses. And overtime, it gets better by adjusting its internal settings, or parameters (weights and biases), to make more accurate predictions.
3. Backpropagation
This is where the real learning happens. After the model makes a prediction, it checks whether it was correct or not. If the prediction is wrong, the model adjusts itself. This process is called backpropagation, where the model learns from its mistakes. It goes back through its layers, adjusting the weights and biases to minimize errors. This happens millions or even billions of times, and with each iteration, the model becomes more accurate.
4. Self-Supervised Learning
The training process uses a technique called self-supervised learning. In self-supervised learning, the model teaches itself by trying to predict missing pieces of information. For example, it predicts the next word in a sentence and based on whether the prediction is right or wrong, it adjusts itself. This helps the model gradually understand language patterns and improves its ability to generate meaningful text.
5. Fine-Tuning
Once a model has been trained on general text data, it’s ready for fine-tuning. Fine-tuning is like a second round of training, where the model is adapted for specific tasks. For example, you might fine-tune a general language model to help write customer service emails or to handle medical questions.
Three common learning models exist:
- Zero-shot learning: This is when the model can answer questions or perform tasks without any extra training. It relies on the general knowledge it learned during training. For example, it can answer trivia questions without being told exactly how to answer them.
- Few-shot learning: Here, you provide the model with a few examples of a specific task. For instance, if you want it to write a poem, you could show it a few poems first. This helps the model improve its performance in that area.
- Fine-tuning: This takes the few shot learning a step further. You give the model lots of specific examples to help it specialize in a particular area. This might be used if you want the model to work in a particular field, like customer support or legal advice.
What Are LLMs Used For?
Now that we know what LLMs are, let’s explore how they’re being used today.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: LLMs like ChatGPT power chatbots that can answer questions, give advice, or even crack jokes. These tools have become popular in customer service, helping businesses interact with customers quickly and efficiently.
- Content Creation: Whether it’s writing blog posts, creating social media captions, or even coming up with poetry, LLMs are great at generating human-like content. For many businesses, this has changed the game by allowing them to create large volumes of content without needing a team of writers.
- Translation: Services like Google Translate use LLMs to provide better translations between languages, offering more accurate and context-aware results compared to older systems.
- Code Generation: LLMs can even understand and generate computer code. Tools like GitHub Copilot help programmers by suggesting code, spotting errors, and even writing functions.
- Healthcare: In medicine, LLMs can assist by summarizing research papers, helping doctors stay on top of the latest studies, or even suggesting possible diagnoses based on symptoms and medical literature.
The Challenges and Concerns
While LLMs are impressive, they do come with their own set of challenges. One of the biggest issues is bias. Since these models learn from data on the internet, they can pick up and even amplify biases found in that data. This means LLMs can sometimes produce results that are unintentionally biased or unfair. For example, an LLM might give biased job recommendations based on past hiring trends that favored certain groups over others.
Another concern is misinformation. LLMs are good at generating text that sounds convincing, but sometimes the information they generate can be completely false. This has led to fears about their potential for spreading fake news or creating misleading content. A great example of this is when LLMs were used to create entirely fake but realistic-looking news articles, making it harder to distinguish between real and fake news.
Finally, there’s the issue of data privacy. Since LLMs are trained on large datasets that may include publicly available information, there’s always a chance that personal or sensitive data could end up being part of the model’s training. This raises concerns about privacy and how data is used. If an LLM accidentally generates personal details about an individual based on its training data, it could lead to serious privacy violations.









